As the business landscape continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly crucial for companies to explore innovative strategies to manage their risks effectively. One such powerful tool that has gained significant traction in recent years is captive insurance. Captive insurance refers to the establishment of an insurance company by a parent organization to provide coverage for its risks, making it a self-insurance alternative. This captive insurer has the advantage of tailoring policies specifically to address the unique needs and risks of its parent company, unlocking significant potential for financial benefits and risk management.
At the forefront of captive insurance is the 831(b) tax code, introduced by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to incentivize small and medium-sized businesses to form their captive insurance companies. With the 831(b) tax code, qualifying captives can benefit from advantageous tax treatment, allowing them to deduct premium payments from their taxable income while only being subject to taxes on their underwriting profits. This particular tax provision has fueled the proliferation of microcaptives, which are captives with annual premiums of $2.3 million or less. The 831(b) tax code has opened doors for smaller companies to unlock the power of captive insurance and leverage it to their advantage.
By embracing captive insurance, businesses can strive for greater control and customization in their risk management strategies. Unlike traditional commercial insurance policies, which are often broad and one-size-fits-all, captive insurance allows companies to have greater involvement in the policy design, coverage limits, and claims process. Tailoring insurance solutions to the specific risks and needs of the parent company enables better protection against potential losses and enhances the ability to secure adequate coverage, even for unique or hard-to-insure risks. This increased control empowers businesses to finely tune their risk management approach, ultimately driving better outcomes and financial gains.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the potential benefits of captive insurance, exploring how it can positively impact a company’s financials, risk management capabilities, and overall operational resilience. We will also navigate the intricacies of the 831(b) tax code, providing invaluable insights into the eligibility criteria, tax advantages, and compliance considerations surrounding microcaptives. Unlocking the full potential of captive insurance requires a comprehensive understanding of the concept, its applications, and the regulatory landscape. So, without further ado, let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the world of captive insurance.
Understanding Captive Insurance
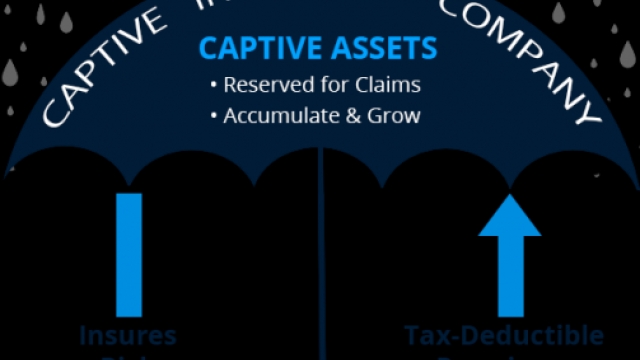
Captive insurance is a form of risk management strategy that allows businesses to create their own insurance company to cover their risks. Under the IRS 831(b) tax code, eligible companies can establish a captive insurance company and receive certain tax advantages. This type of insurance, also known as a microcaptive, provides businesses with more control and flexibility over their insurance coverage.
By setting up a captive insurance company, businesses can have greater say in the types of risks they want to insure against and the terms of their insurance policies. Instead of relying solely on traditional insurance carriers, captives enable businesses to customize their coverage to suit their specific needs and risk profiles. This level of control can lead to more favorable coverage terms and potentially lower costs in the long run.
The IRS 831(b) tax code provides certain tax benefits for captive insurance companies with annual premiums below a specific threshold. These small captives allow businesses to receive favorable tax treatment, such as exemption from federal income tax on underwriting profits. This tax advantage can offer significant savings for businesses that qualify under the IRS guidelines.
In summary, captive insurance offers businesses a powerful tool for risk management and financial planning. By establishing a captive insurance company, businesses can gain more control over their insurance coverage while potentially realizing tax benefits. Understanding the intricacies of captive insurance and the applicable tax regulations is crucial for businesses looking to unlock the full potential of this risk management strategy.
The Benefits of 831b Captive Insurance
Captive insurance, particularly the 831b tax code, presents a range of advantages for businesses exploring alternative risk management strategies. Here, we delve into some of the notable benefits a microcaptive can offer:
Enhanced Risk Management:
By forming a captive insurance company under the 831b tax code, businesses gain greater control over their risk exposures. With the ability to tailor insurance coverages to their specific needs, companies can fill gaps in existing commercial policies and mitigate risks that are typically challenging to insure in the traditional market. This affords them a more comprehensive and customized risk management approach.

Potential Cost Savings:
Get The Best Price
Utilizing a captive insurance structure can lead to significant cost savings in several ways. Firstly, by retaining their own risk, businesses potentially avoid overpriced premiums charged by commercial insurers. Moreover, captive insurance allows for the use of more favorable loss control and claim management strategies, potentially resulting in reduced claims costs over time. These savings directly contribute to the overall financial well-being of the captive owner.
Tax Advantages:
The 831b tax code introduces tax advantages for microcaptives, providing additional incentives for businesses considering this alternative risk management solution. Under this code, captives that meet certain requirements can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, with premiums received considered as tax-exempt. This can lead to significant tax savings for captive owners, allowing them to retain more capital to fund operational growth and risk management activities.
In conclusion, 831b captive insurance offers businesses the opportunity to take control of their risk exposures while potentially enjoying cost savings and tax advantages. However, it’s important for companies to thoroughly evaluate their unique circumstances and consult with experienced professionals to ensure that captive insurance is the right fit for their risk management strategy.
Navigating the IRS 831b Tax Code
To ensure a smooth experience in utilizing captive insurance, it is crucial to understand the IRS 831b Tax Code and its implications. This tax code specifically applies to captive insurance companies operating as microcaptives. By grasping the intricacies of this code, businesses can unlock the full potential of captive insurance.
The IRS 831b Tax Code provides a unique opportunity for qualifying small captive insurance companies to enjoy certain tax benefits. Under this code, if a captive insurance company meets the specified criteria, it may elect to be taxed only on its investment income. This means that the premiums collected by the captive insurer can be excluded from taxable income, thereby reducing the overall tax liability for the business.
However, it is essential to note that the IRS places strict requirements on companies seeking to take advantage of the 831b Tax Code. Microcaptives must meet specific qualifying criteria and adhere to ongoing compliance regulations to maintain their eligibility. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in the loss of tax benefits and potential penalties.
To navigate the IRS 831b Tax Code successfully, businesses should seek the expertise of qualified professionals who specialize in captive insurance and tax compliance. These professionals can provide valuable guidance on structuring the captive insurance arrangement to align with the code’s requirements. Their knowledge and experience will help businesses maximize the benefits while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the IRS 831b Tax Code is vital for businesses exploring the potential of captive insurance. By electing to be taxed under this code, companies can enjoy tax advantages and mitigate risks effectively. However, businesses must ensure they meet the qualifying criteria and comply with ongoing regulations to fully harness the power of captive insurance within the framework of the IRS 831b Tax Code.